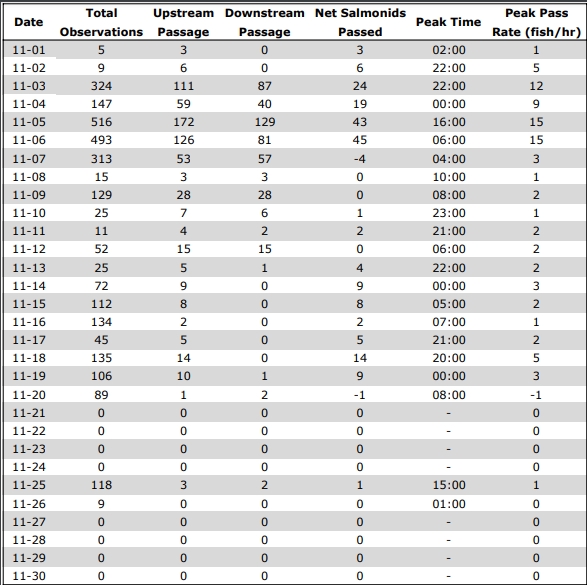
The biology, microhabitat use and migratory behaviour of greenside darters (Etheostoma blennioides) was studied at the Mannheim Weir
Black Redhorse Habitat Preferences
We have been working in conjunction with Fisheries and Oceans Canada to study egg development, early life history
Greater Redhorse Ecology
In 1997, we began studying greater redhorse (Moxostoma valenciennesi) spawning habitat, spawning behaviour, fecundity, egg and larval development, as well as post-spawn movements and habitat use. We continued this work into 2006 with a 6-year radiotracking and underwater videography study of redhorse in the Grand River.
Wavy-Rayed Lampmussel Monitoring
In a few rivers in Canada including the Grand River, Ontario, this endangered unionid bivalve uses lures to attract smallmouth bass as part of its reproductive cycle. When a fish approaches the lure (one lure type imitates a leach, one imitates a crayfish and the other lure type imitates a darter – see pictures below), the mussel expels numerous glochidia into the mouth of a smallmouth bass. The glochidia are larval mussels that attach to the gill filaments of the fish for several months. During this period, the fish carry the mussels upstream, and likely use fishways to transport mussels upstream over barriers such as the Mannheim weir.
Silver Shiner Size-Class Structure, Habitat Utilization, Movement and Persistence in an Urbanized Fragment of a Great Lakes Tributary
Silver Shiners were captured and habitat was characterized from 38 locations in the Grand River during the summer and autumn of 2013
Integrated Wetland Management- Lake Chubsucker
Our initial contract with Environment Canada (EC) / Canadian Wildlife Service (CWS) involved relocation of native fish and disposal of non-native invasive species during a planned drawdown of the St. Clair National Wildlife Area
Razorback Sucker Telemetry
Biotactic assisted Bio-West (Utah) with the set-up of a combined sonic and radio-telemetry project of federally endangered razorback suckers
Spotted Gar Habitat Utilization
In May of 2007 we initiated a radio telemetry project for spotted gar in Rondeau Bay on Lake Erie
Blue Sucker Tracking
In October 2004 we implanted thirty Texas state endangered blue suckers (Cycleptus elongatus) with radio transmitters that we (Bio-West, Austin and Biotactic) monitored continuously
Black Redhorse Ecology
In October 2007 a large pool in the Grand River near Kitchener, Ontario was sampled using seine nets for adult black